Aircraft Traffic Pattern
Aircraft Traffic Pattern - The faa also lists a conventional midfield downwind entry as acceptable, with the midfield crossing done at pattern altitude. Web the standard traffic pattern is a rectangular pattern consisting of an upwind, crosswind, downwind, and final approach leg. Web so here we have got to the one of the main phases of a basic flying traffic pattern which usually consists of the departure leg or upwind leg, crosswind leg, downwind leg, the main leg, and final approach. Web wind and traffic pattern. Another term commonly used is “uncontrolled airport.” 6.2 common traffic advisory frequency (ctaf). Web the faa now wants planes to enter at 500 feet above pattern altitude and then make a reverse teardrop to join the downwind, initiating the turn only after descending to pattern altitude. An airfield traffic pattern helps to “direct traffic” over an airfield. Right pattern information is listed for an airport in a vfr sectional, with the abbreviation “rp” followed by the runway number. Know where to look for details on the pattern. Far 91.123 requires you to follow all atc clearances and instructions. Web the traffic pattern, more commonly referred to just as “the pattern,” allows vfr pilots to enter or exit the airport area in an organized manner, keeping all of the aircraft safe and on a flight path where the pilots can see. Web the traffic patterns provide specific routes for takeoffs, departures, arrivals, and landings. Web an airfield traffic pattern. Your safety is assured by vertical rather than lateral separation. Pilots assume that other pilots have knowledge of it and are following its maneuvers. Web the traffic pattern, more commonly referred to just as “the pattern,” allows vfr pilots to enter or exit the airport area in an organized manner, keeping all of the aircraft safe and on a flight. The faa also lists a conventional midfield downwind entry as acceptable, with the midfield crossing done at pattern altitude. Find further pattern information in the chart supplement, including traffic pattern altitude. Know where to look for details on the pattern. Unless the airport displays approved visual markings indicating that turns should be made to the right, the pilot should make. The exact nature of each airport traffic pattern is dependent on the runway in use, wind conditions, obstructions, and other factors. Web since most traffic patterns are between 800 and 1,000 feet above ground level (agl) &mdash don't forget that faster, heavier, or turbine aircraft typically fly the traffic pattern at 1,500 agl &mdash this should put you around 2,000. The exact nature of each airport traffic pattern is dependent on the runway in use, wind conditions (which determine the runway in use), obstructions, and other factors. And what about the air traffic pattern altitude? Another term commonly used is “uncontrolled airport.” 6.2 common traffic advisory frequency (ctaf). Far 91.123 requires you to follow all atc clearances and instructions. Pilots. Web the traffic pattern, more commonly referred to just as “the pattern,” allows vfr pilots to enter or exit the airport area in an organized manner, keeping all of the aircraft safe and on a flight path where the pilots can see. Even at unfamiliar fields, a pilot can anticipate the direction of traffic and enter the pattern safely. Unless. During pattern work, one circuit might be to the left and the next to the right. The faa also lists a conventional midfield downwind entry as acceptable, with the midfield crossing done at pattern altitude. Web traffic patterns are an essential part of every flight, and exercising good aeronautical judgment is necessary when flying them. The exact nature of each. The components of a typical traffic pattern are upwind leg, crosswind leg, downwind leg, base leg, and final approach. Web entering the pattern on the upwind leg allows a pilot time to visually identify the location of all other aircraft in the pattern. And what about the air traffic pattern altitude? If there is a place to be overly cautious,. Right pattern information is listed for an airport in a vfr sectional, with the abbreviation “rp” followed by the runway number. Web the faa now wants planes to enter at 500 feet above pattern altitude and then make a reverse teardrop to join the downwind, initiating the turn only after descending to pattern altitude. Web an airfield traffic pattern is. Web at nontowered airports, traffic patterns establish an orderly flow for aircraft taking off and landing. Another term commonly used is “uncontrolled airport.” 6.2 common traffic advisory frequency (ctaf). Airports without control towers or airports with control towers that are not operating. Web wind and traffic pattern. Web since most traffic patterns are between 800 and 1,000 feet above ground. The faa also lists a conventional midfield downwind entry as acceptable, with the midfield crossing done at pattern altitude. Web the standard traffic pattern is a rectangular pattern consisting of an upwind, crosswind, downwind, and final approach leg. Web operations at a towered airport can be quite different. By entering the traffic pattern on the upwind leg, a pilot has time to establish visual contact with traffic while having flexibility to alter the pattern and airspeed as needed to maintain safe separation. Right pattern information is listed for an airport in a vfr sectional, with the abbreviation “rp” followed by the runway number. You can find traffic pattern information for specific airports on a sectional chart and in the chart supplement (see “which way?” p. Web entering the pattern on the upwind leg allows a pilot time to visually identify the location of all other aircraft in the pattern. Find further pattern information in the chart supplement, including traffic pattern altitude. Web an airport traffic pattern includes the direction and altitude of the pattern and procedures for entering and leaving the pattern. Web an airport traffic pattern includes the direction and altitude of the pattern and procedures for entering and leaving the pattern. Web traffic patterns provide procedures for takeoffs, departures, arrivals, and landings. Web wind and traffic pattern. At an airport , the pattern (or circuit ) is a standard path for coordinating air traffic. Web the recommended entry position to an airport traffic pattern is to enter 45° at the midpoint of the downwind leg at traffic pattern altitude. Web the traffic pattern, more commonly referred to just as “the pattern,” allows vfr pilots to enter or exit the airport area in an organized manner, keeping all of the aircraft safe and on a flight path where the pilots can see. Know where to look for details on the pattern.
Important Guide to Entering the Traffic Pattern Safely! Lets Fly VFR

Procedures and Airport Operations Traffic Patterns Learn to Fly Blog

Traffic Pattern New Traffic Pattern For Buffalo Commuters

Understanding the Traffic Pattern Pilot Institute
/Traffic_patterns_depicted_in_FAA-H-8083-25-56a058ce3df78cafdaa1229b.jpg)
How to Fly a General Aviation Traffic Pattern
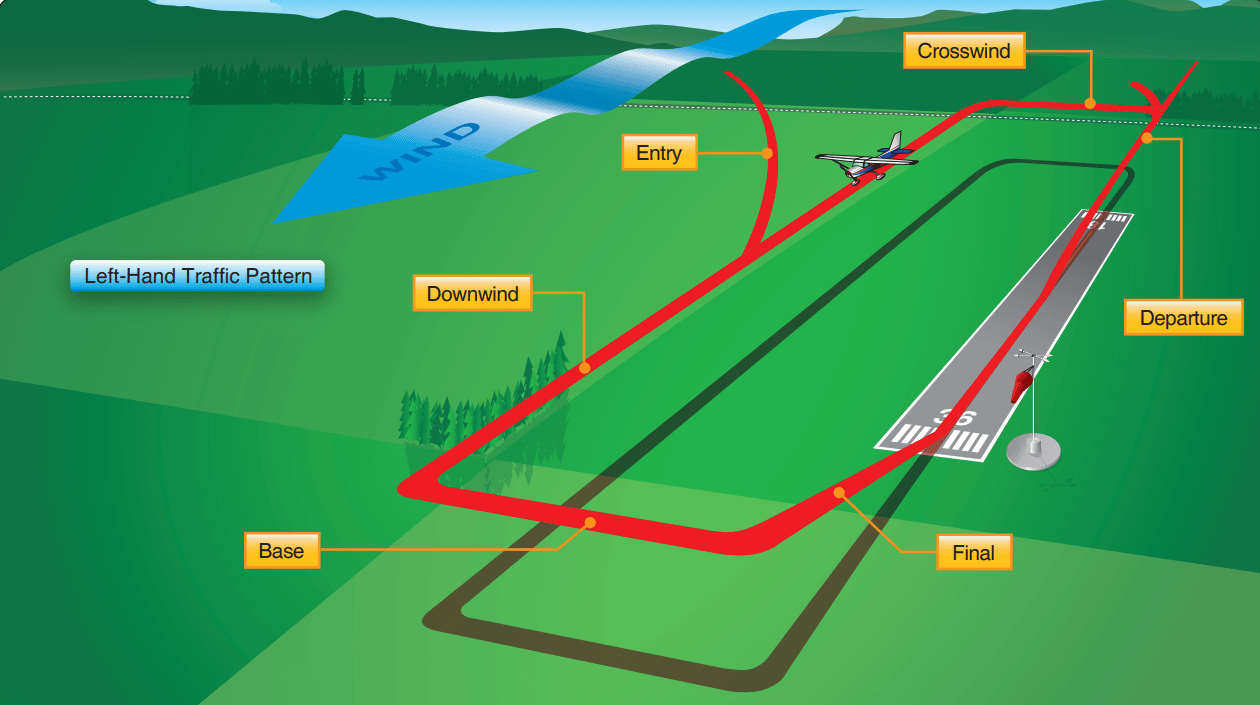
Important Guide to Entering the Traffic Pattern Safely! Lets Fly VFR

Understanding the Traffic Pattern Pilot Institute

Everything You Should Know About the Airport Traffic Pattern

Procedures and Airport Operations Traffic Patterns Learn to Fly Blog

Simulating the traffic pattern and goarounds Armstrong Aviation
Unless The Airport Displays Approved Visual Markings Indicating That Turns Should Be Made To The Right, The Pilot Should Make All Turns In The Pattern To The Left.
And What About The Air Traffic Pattern Altitude?
If There Is A Place To Be Overly Cautious, It Is In The Pattern At A Nontowered Airport—Where Arriving And Departing Traffic Mix With Students Making Circuits For Takeoff And Landing Practice.
The Exact Nature Of Each Airport Traffic Pattern Is Dependent On The Runway In Use, Wind Conditions (Which Determine The Runway In Use), Obstructions, And Other Factors.
Related Post: